World Tuberculosis Day: End Tuberculosis
World Tuberculosis Day is organized every year by the World Health Organization (WHO). This year’s theme was ” It’s time to end tuberculosis.”
The reason behind the choice of this particular date was to commemorate the day Robert Koch told the world that he had identified the microorganism that causes the disease. Mycobacterium tuberculosis is a bacteria in the form of a bacillus. It is also informally known as ‘Koch’s bacillus’.
The discovery of this disease took place in the year 1882, but only 100 years later the celebration of World Tuberculosis Day began. This event, sponsored by the International Union Against Tuberculosis and Lung Disease (English link) has been held since March 24, 1982.
The disease infects about 10 million people in the world every year, more than 10% of whom die. That is why this disease is in the top 10 of most common causes of death in the world. It is the leading cause of death among people with HIV.
Eight countries have been responsible for the highest number of new cases per year in recent years . These include India, the Philippines, Pakistan and Nigeria. Asia and Africa are the two continents where tuberculosis is most commonly found.
What is tuberculosis?
World Tuberculosis Day aims to raise awareness of a disease that many are unaware of, although it is quite common. It’s not high on the agenda of public health organizations, which puts it in the background.
However, as we can see in the statistics, it is a major problem for healthcare. The pulmonary complications become chronic and the ability to infect HIV patients places a great burden on their treatment.
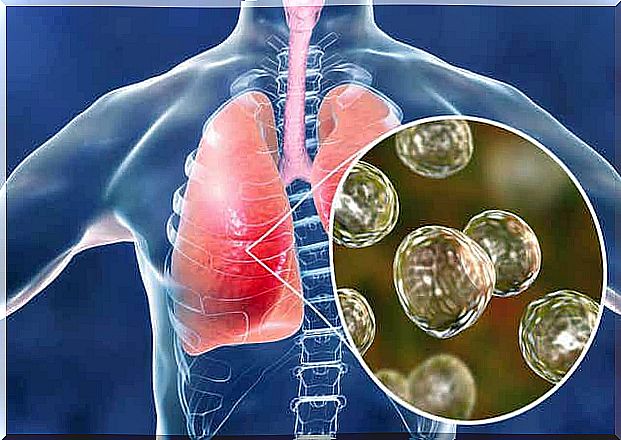
Tuberculosis is defined as the pathology caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and arises when this bacillus enters the organism and settles in the lungs. There it produces a reaction that forms nodules in the lung tissue.
Transmission takes place by air. The bacteria move through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes and even when they spit. People who are most affected are those who spend a lot of time with the sick person.
The bacillus in question can be present in a human organism for a long time without causing any symptoms of disease. It is even possible to carry the bacillus with you for a lifetime without actually suffering from tuberculosis. But if your immune system is weakened for some reason, this allows activation.
Although tuberculosis primarily affects lung tissue, there are other tissues that may show signs, although this is significantly less common. For example, there are:
- bone tuberculosis
- urinary tuberculosis
- digestive tract tuberculosis
The Symptoms of Tuberculosis

When pulmonary tuberculosis develops, the symptoms begin. An infected person with an active disease is contagious if he does not undergo any kind of treatment, as we will see below. The classic symptoms of the pathology include:
- Cough: persistent and productive, with some blood in it – called hemoptysis or hemoptysis.
- Chest pain: associated with the breathing movements.
- Weight Loss: Striking and progressive, to over 20 pounds.
- Nocturnal fever attacks: One of the hallmarks of elevated body temperature is that it appears mainly at night and early in the morning.
In children it is different because the symptoms are not so obvious. It is possible to confuse the onset with other more common childhood illnesses, such as bacterial pneumonia or the flu.
World Tuberculosis Day: The Problem of Bacterial Resistance
World Tuberculosis Day aims not only to raise awareness of the disease, but also to raise awareness of the difficulties involved in its treatment. Worrying developments have been seen in recent decades due to the resistance that the bacteria exhibit.
Although the treatment of tuberculosis has traditionally been done with antibiotics, the bacillus has developed resistance mechanisms (Spanish link). These mechanisms made it necessary to change the treatment plan.
This led to the development of the concept of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis, defined as the disease unresponsive to two first-line antibiotics: rifampicin and isoniazid. When doctors detect this situation, it is necessary to switch to the use of drugs that are more difficult to obtain and have a longer duration of use, even up to two years of use.
What to do on World Tuberculosis Day?
Due to the frequency of this disease, you can be sure to meet people who suffer from it. It is one of the most common diseases in the world and a leading cause of death. Therefore, it should get the attention it deserves.
So, on World Tuberculosis Day, we can begin to better inform ourselves about the disease and perhaps find out which associations in our area are involved with this disease. There are several ways to help and provide assistance.