How To Raise Children With Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is a chronic disease. However, when properly controlled, it does not necessarily decrease the quality of life of those affected. Children with diabetes need specific care, but they can still lead normal lives.
Today we will explain a little more about this disease. We also give you advice on how to raise a child with this condition.
Type 1 diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease that often develops during childhood. It affects the cells that produce insulin. In general, it represents between 10% of diabetes cases and often develops between the ages of 10 and 15 years.
In people with type 1 diabetes, the pancreas loses its ability to make insulin because the immune system itself attacks and destroys the beta cells that synthesize and secrete insulin.
Insulin, a peptide hormone, regulates carbohydrate metabolism by promoting carbohydrate absorption. That includes storing glucose from the blood in the liver and fat cells. In addition, it supplies the skeletal muscle cells that need glucose to produce energy. It is therefore vital to counteract this deficiency of insulin.
Currently, there is no cure or cure for type 1 diabetes. However, it can be treated by focusing treatment on controlling blood glucose levels. You can do this by taking insulin regularly and living a healthy lifestyle.
The underlying cause of type 1 diabetes is uncertain. However, some believe that factors such as genetics and certain viruses contribute to the appearance of the symptoms. Although type 1 diabetes usually develops during childhood or pre-adolescence, it can also appear in adulthood.
Advice for raising children with type 1 diabetes

Below we will present some general recommendations so that both your family and the affected child can cope with type 1 diabetes and so that the disease does not jeopardize his quality of life.
1. Increase your knowledge of type 1 diabetes
When your child is diagnosed, it is very important that he learns the basic aspects of the disease. It is also crucial that you help him carry out a normalization process in his immediate environment. This helps him adjust to his new lifestyle.
Both family members and teachers should know the procedures that may be necessary and participate in the correct pharmacological and emotional care of the child.
2. Understand the Diet Guidelines
Food intake is one of the keys when treating children with type 1 diabetes. It is therefore very important that they maintain control and follow specific rules both at home and at school .
The main things to keep in mind are:
- A balanced diet: The child needs to know how to control the amount of carbohydrates he ingests, as this must be in balance with the amount of insulin being injected.
- The intake of too many calories and fat should be avoided as this can lead to obesity.
- Fruits and vegetables, as well as high-quality protein and complex carbohydrates, should all be in all his meals.
- He should limit his consumption of simple carbohydrates. This is essential to avoid sudden, sharp increases in blood sugar. Foods to avoid due to their high added sugar content include ultra-processed products such as syrups and sodas.
- Parents should ask teachers about the weekly menus from the school cafeteria when eating at school. In addition, if the child is very young, educators should know that these children should have a mid-morning and mid-afternoon snack so that their blood sugar levels remain stable.
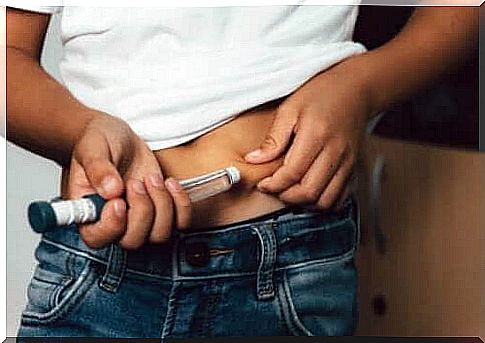
3. Use pharmacological treatment
Children with type 1 diabetes usually need to inject insulin several times a day. Often a fast-acting insulin is chosen for every meal and a slow-acting type of insulin once or twice a day.
Try to administer this in a relaxed environment and preferably at home. Teachers should know the procedure if the child is too young and needs help giving the injections.
4. Blood Sugar Control
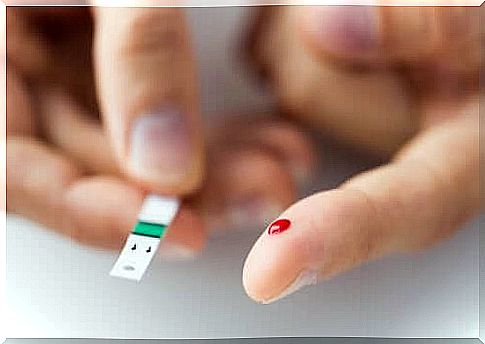
Children with diabetes should be checked periodically, with a small prick in their index finger, to know what their blood glucose levels are. A child can learn to perform his periodic sugar checks with a portable glucose meter.
At school , they should be able to do this in the classroom or some other place they feel comfortable in, such as the teachers’ lounge or another separate area where they can be alone.
5. Exercise for children with diabetes
Children with diabetes can perform the same physical activities as other children their age. They must follow a number of guidelines, such as:
- They should measure their blood sugar levels before and after exercise and then adjust their meals and/or the amount of insulin they inject if necessary.
- Parents or teachers who are present during the child’s physical activities should have quick access to foods rich in carbohydrates. This is in case of a sudden drop in blood sugar (hypoglycaemia).
- Dextrose is preferred because it is absorbed the fastest. Afterwards, a snack can be eaten so that the blood sugar level remains stable.
Summary about raising children with type 1 diabetes
The current options used in managing the problems of type 1 diabetes can contribute to a good quality of life for those who suffer from it.
In the case of children , all responsible adults around them should know the features of the disease. This is to be able to guide them and help them control their blood sugar levels.