Different Types Of Dystonia In Children

Dystonia in children is a movement disorder that causes involuntary muscle contractions. These contractions cause muscle twitching and repetitive movements.
This condition can occur as a result of a genetic mutation, a condition, or a drug. So some people inherit this condition, while others develop it as a result of another illness or taking certain medications.
It is relatively common in children. According to the Spanish Society of Neurology (SEN), dystonia is the third most common type of movement disorder in children. In this article we explain what it is and how to diagnose it.
Types of Dystonia in Children
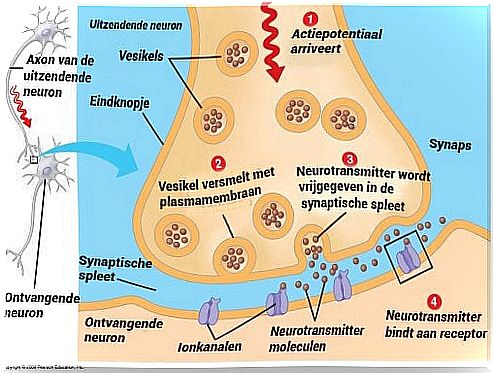
Depending on how many parts of the body they affect, these types of childhood dystonia can be focal, segmental, multifocal, or generalized. Experts also classify them according to their cause:
Hereditary (primary dystonia)
This is the most common form of dystonia in children and is related to specific genetic defects. Within these defects we can highlight the following:
- Isolated generalized dystonia: This type is not associated with other neurological symptoms. The gene most frequently altered here is the DYT1 gene. The average age of onset is 12 years. It is important to know that most symptoms occur in the legs.
- Dopa-sensitive dystonia: Also known as Segawa syndrome, this is one of the few that doctors can treat. It starts around age 6 with a gait disorder and is more common in girls. Furthermore, the symptoms may fluctuate throughout the day.
Transient developmental dystonia
- Benign Dystonia in Infants: This is seen in infants 3 to 8 months of age. This type does not affect a child’s psychomotor development. Everything usually returns to normal when the child reaches the age of one.
- Benign paroxysmal torticollis: This is a rare type and is associated with vomiting and unsteady walking. However, it usually improves after five years.
Hereditary degenerative dysplasia
These types are created by mutations of genes involved in metabolism and are much more complex. Pathologies such as Lesch Nyhan disease and Niemann Pick disease stand out here.
Secondary dystonia
These are the types of dystonia that are caused by other underlying diseases or conditions. They can occur due to infections, tumors, structural defects, toxins, drugs, etc. Therefore, it is essential to correctly identify and treat the cause.
Diagnosing Dystonia in Children
First of all, doctors need to rule out secondary dystonias. To do this, they conduct toxicology and neuroimaging studies and prepare a comprehensive medical history of the patient. Among the imaging tests, computed tomography and resonance imaging are the main ones.
Physicians also need to do complementary metabolic and genetic research. These studies may also include an electromyogram and an electroneurogram. In this way, doctors can determine an accurate prognosis and treatment.
Treatment of dystonia in children
First of all, if there is generalized dystonia, doctors will administer anticholinergics. Two of the most commonly used are trihexyphenidyl and benztropine. These will reduce spasms by blocking specific nerve impulses.
However, they also have numerous side effects, including confusion, drowsiness, dry mouth, blurred vision, dizziness, and so on. A mild anxiolytic, such as clonazepam, can often help. If the generalized dystonia is severe or unresponsive to medication, deep brain stimulation may be performed.
Children with dopa-sensitive dystonia improve significantly with levodopa and carbidopa treatment. If their symptoms affect only one or a few areas of the body, doctors may inject botulinum toxin into the overactive muscles. This weakens muscle contraction but does not affect the nerves.
Conclusion
It is important to consult the pediatrician if you notice involuntary muscle movements in your child. They may have a movement disorder, such as dystonia.
This condition usually disappears after a few months without any consequences. However, you should not ignore them. Dystonias that last into adulthood can cause permanent disabilities.