Detecting And Preventing Deep Vein Thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT), or phlebothrombosis, occurs when a blood clot called a thrombus forms in one or more deep veins in the body. It usually affects the legs, although it can arise in other parts of the body as well.
This condition can occur if you have certain conditions that affect the way the blood clots. You can also develop it if you don’t move for long periods. For example, it can occur after surgery or an accident.
Deep vein thrombosis is a serious condition. The blood clots that form in the veins can move through the bloodstream and end up in the lungs.
Once there, they can cut off blood flow and cause a pulmonary embolism. Similarly, the blood clots can move toward your heart. In these cases, a heart attack can occur.
What Causes Deep Vein Thrombosis?
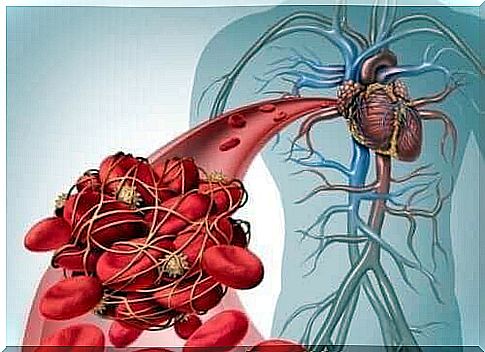
When a person has a deep vein thrombosis, blood cannot flow properly through the arteries furthest from the heart . It then accumulates and causes edema and swelling.
The blood going from the heart to the feet flows through the arteries. Once it arrives at the feet, it returns through the veins back to the heart. From there it flows to the lungs to oxygenate.
Blood clots that can cause a deep vein thrombosis develop as a result of an abnormality. It may be that the blood does not circulate properly or that the clotting is promoted. These problems can occur, for example, after surgery or as a side effect of certain medicines, but also due to too little exercise.
In addition, several risk factors can make a person more susceptible to this condition. For example, consider the following factors:
- Genetics: Some people have an inherited condition that leads to circulation problems.
- Prolonged rest: this may be due to hospitalization, for example.
- Injury or surgery, as we mentioned above.
- Pregnancy, overweight or obesity.
- Smoking and other unhealthy habits.
How is deep vein thrombosis detected?
There are many tests to detect deep vein thrombosis. They range from imaging techniques to diagnosis through blood tests.
First of all, it is important to note that there are other conditions with signs and symptoms similar to those of deep vein thrombosis. For example, think of:
- pulmonary embolism.
- muscle injuries.
- cellulite.
- inflammation of the veins just under the skin.
It is therefore important to do special tests to locate the clots in the veins in order to distinguish this disease from other diseases. We will discuss below the tests that can be done.
Duplex Ultrasound
This is a test that uses sound waves to generate images to observe blood flow through the veins. It can detect blockages or blood clots in deeper veins. It is thus the standard imaging test for the diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis.
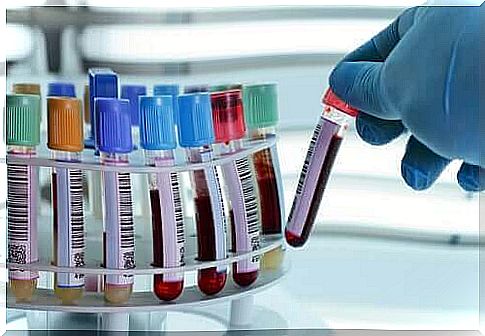
D-dimer test in deep vein thrombosis
This test consists of a blood test that measures a certain substance that is released into the blood when a clot is dissolved in the blood. A negative result means that it is someone who probably does not have this condition and vice versa.
phlebography
This is the most accurate test to diagnose blood clots. However, it is an invasive procedure, which means that doctors must use instruments to manipulate the body. It is a special type of X-ray in which the doctor injects contrast dye into a large vein of the foot or ankle. This way they can see the blood flow from the deep veins.
MRI and CT scan
These two tests show images and help doctors diagnose and treat a variety of conditions. The images show veins and any clots in them. However, these tests are not commonly used to diagnose this condition. However, it is an available tool that can be used if necessary.
Prevention of the condition

The prevention of DVT is based on improving blood flow returning to the heart. It is therefore important to consult your doctor so that he or she can recommend an exercise routine.
It is also recommended to raise your legs regularly to facilitate circulation. In this regard, a person with this condition will be more comfortable having the part of the mattress on which the legs rest slightly up. This will help you rest with the legs in a slightly elevated position.
- If you smoke, try to quit. Tobacco is a risk factor for many heart conditions.
- Doctors also recommend exercising for at least 30 minutes a day at least 3 days a week.
- It may also be helpful to eat more foods that prevent blood clotting.
- If necessary, the doctor can prescribe the use of anticoagulants to prevent these types of problems.