A CT Scan: The Procedure, Uses And The Risks
Imaging studies such as an arteriography and X-rays are helpful when it comes to looking at the internal structures of the body. Specialists often use a CT scan for this.
The body is analyzed from different angles using X-rays. These photos are superimposed by the computer to create a 3D image. These cross-sections show certain problems better than one-dimensional X-rays.
CT scan are non-invasive. They use a scanning method to generate a two- or three-dimensional image of the internal structure of an object or body. Medical professionals often use this procedure to assess for internal injuries. However, there are other areas that use it as well, such as industry and geology.
Several studies state that a CT scan is one of the most commonly used methods of looking at people’s internal organs (Spanish link). This procedure has improved a lot since it was first introduced in 1971.
Originally it only showed images of the brain, but now one can scan every anatomical region of the body. Let’s take a look at the possibilities and the course of this research.
What is a CT scan used for?
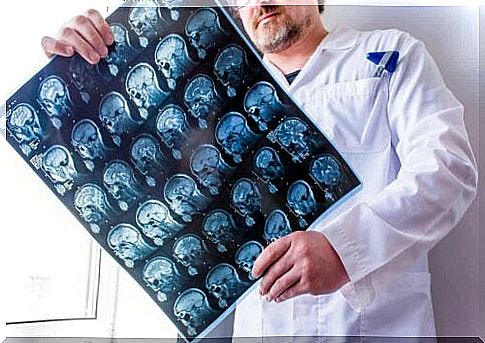
This imaging test has a wide range of applications in different fields of medicine, such as oncology, cardiology and traumatology. It can also be used by doctors for diagnosis and follow-up of patients suffering from various conditions. In addition, this technique is useful in the planning of radiation treatments.
A CT scan shows the condition of both soft organs and bone tissue. Therefore, this technique can be used to evaluate the liver, kidneys and brain, as well as showing the bones around it. As a result, multiple problems can be detected using this test.
This is the preferred method of research in the evaluation of various cancers as it can confirm the presence and precise location of a tumor. It is also possible to study its characteristics, which allows to observe its size and possible spread to nearby tissue.
Tomography is also useful in studying spinal injuries and in evaluating bone density. Finally, we will state that it is even very useful in exploring the head. It is a method with which brain haemorrhages can be detected.
Preparation in advance
A CT scan is a very quick and minimally invasive procedure. A patient does not have to go through detailed preparation for it. However, one should wear comfortable clothes as one may need to take them off and put on a hospital gown.
Also, metal objects can affect the image in the CT scan, causing unreliable results. Therefore, before the scan, the patient must remove the glasses, earrings, rings, piercings, dentures or other metal objects.
In certain situations, the medical professional may also inject a contrast agent to better assess a particular area. If this is the case, doctors recommend that you do not drink or eat anything before the scan.
In addition, the doctor should be aware of any allergies. People with heart, kidney or thyroid problems and (possibly) pregnant women should inform their specialist about this in advance. All of these situations increase the risk of side effects during the scan. In the case of women who are pregnant, this is a contraindication for having X-rays taken.
How does a CT scan work?
First, the nurse will ask the patient to undress and put on a hospital gown. Sometimes loose clothing is sufficient as long as there is no metal on it. If someone needs a contrast agent for the test, the nurse or doctor will administer it orally, intravenously, or through an enema.
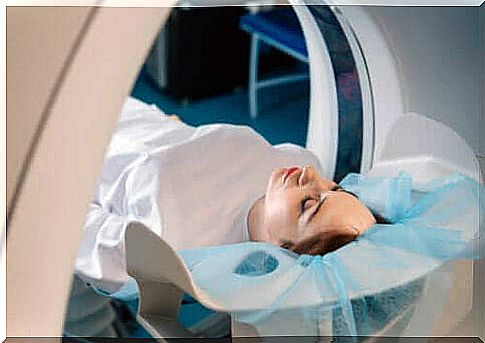
A CT scanner is a large, donut-shaped machine with a bed and a central tunnel. The patient will usually lie on their back or in some cases, lie on their side or face down. The bed may have straps and pillows to keep the body in the correct position.
At the start of the CT scan, the bed will move quickly to determine the area the machine should scan. Then the bed slowly enters the scanner and scans the area. In some cases it is necessary for the bed to go back and forth through the machine several times.
It is important that the patient does not move during the scan. That’s because any movement can cause errors called artifacts. Some scans even require the patient to hold their breath for a few seconds.
When the examination is complete, it is necessary to wait for the doctor to confirm that the images are of good quality. Then results are clear in a short time and the evaluation usually takes about 30 minutes.
Potential Risks and Complications
Anxiety attacks are one of the most common problems with a CT scan. This is common in people who suffer from claustrophobia and in young children. In general, the doctor will give these people a mild sedative before the scan.
In addition, this study exposes patients to a type of radiation called ionizing radiation. Some studies link high doses of this type of energy to the development of cellular mutations (Spanish link). However, CT scans use very low levels of this radiation.
Nevertheless, a CT scan is a widely used and safe examination. That’s because its benefits far outweigh its risks. However, specialists should try all other options that use less radiation before requesting such a scan.
Understanding the results of a CT scan
Within minutes of completing the exam, the radiologist will discuss the results with the doctor. They will now usually store the images in a digital file so that one can view them on a computer screen.
The radiologist is the specialist in charge of supervising and interpreting this examination. They are therefore the ones who can detect any deviations. After analyzing the results, they prepare a report. They then give that report to the patient’s attending physician.
A study with more benefits than risks
CT scans are imaging studies that use X-rays to look at soft organs and bone tissue. However, they expose people to up to 100 times more radiation than traditional X-rays. That could pose certain risks in the long run.
The risk of damage is greater in children than in adults, because their cells divide faster. Despite all that, this research remains very useful in detecting multiple diseases. That’s because the benefits far outweigh the risks.